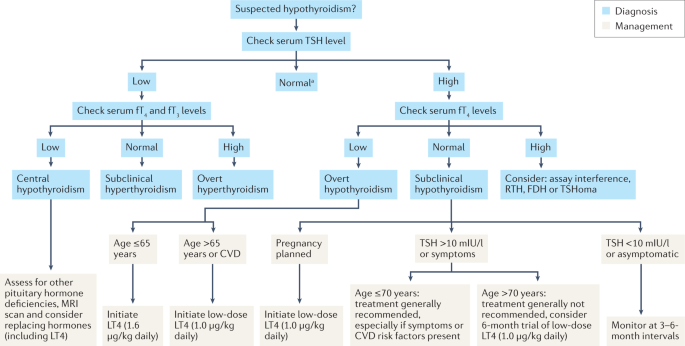
When it comes to thyroid health, a thorough understanding of the roles that T3, T4 and TSH play becomes pivotal. Thyroid function tests like TSH, Free thyroxine, and free triiodothyronine are extremely vital for the diagnosis of thyroid disorders. Whether you are experiencing symptoms like fatigue, weight change or mood swings, a comprehensive knowledge of these tests can help to uncover your thyroid health problems and provide you with the essential information for effective management of the diseases. In this article, we shall have a closer look at T3, T4, TSH testing in thyroid diagnosis and other aspects.
Understanding T3 and T4 Hormones
T3 and T4 are hormones produced in the thyroid gland and each contributing differently to regulating speed of metabolism, activity levels, and overall bodily functions. The malfunction of the thyroid gland can lead to different types of thyroid diseases, such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism or thyroid nodules. Testing the levels of these hormones allows healthcare providers to evaluate the function of the thyroid and identify any irregularities.
Role of TSH in Thyroid Function
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) is described to be the primary derivative of thyroid function. Secreted by the pituitary, TSH activates the thyroid gland, and T3 and T4 are thus formed. Usually, a high level of TSH points to a hypoactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) that fails to make enough thyroid hormones needed. Contrastingly, low TSH may point to the inappropriately active thyroid (hyperthyroidism) that consists of the overproduction of hormones.
The Functions of T3 and T4
The two predominant thyroid hormones, which are also referred to as T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), have the responsibility of regulating metabolism and energy production. T4 is mainly produced by the thyroid gland and is the immediate predecessor of T3. It undergoes activation in several tissues of the body into the more active thyroid hormone,T3. T3 is the version of thyroid hormone that the highest influences the metabolism and the performance of all cells.
Importance of T3 and T4 Levels in Diagnosis
When assessing thyroid function, it is essential to consider both T3 and T4 levels to get the most complete reading on thyroid health. The active thyroid hormones T3 and T4 levels may fall and the patient could have hypothyroidism or alternatively may be elevated in which case hyperthyroidism is diagnosed. Still, the interpretation involves taking account of the patient’s own characteristics and concurrency with other diseases.
T3, T4, TSH testing Procedures
It is common to conduct T3, T4, TSH tests using blood tests. Testing procedures like these are just efforts that are not invasive and provide necessary information about how the thyroid gland functions. To achieve precise results, adhering to any pre-test instructions made by your healthcare provider before, as instructed, such as the need to fast or altering your medication dose, is the best option.
Monitoring and Treatment
Also, the T3, T4, TSH tests are used both for detecting thyroid disorders and treatment monitoring. During the therapy when the failing thyroid gland is replaced by the medication the patient regularly undergoes the testing to ensure that the hormone level is within the target range which in its turn optimizes symptom management providing better comfort level.
FAQs regarding T3, T4, TSH testing
Now, let’s address some commonly asked questions about T3, T4, TSH testing:
- How often should T3, T4, TSH testing be performed? The frequency of testing on an individual basis depends on individual circumstances and on thyroid diseases. In general, patients with thyroid function in a stable state undergo testing at their demand or as recommended by their healthcare providers. On the other hand, patients with thyroid conditions or those being treated may require more consistent evaluation.
- Is it possible to see T3, T4, and TSH levels shifting? Indeed, the normal range of thyroid hormone levels can be affected by factors such as stress, illness, medications and hormonal shifts (either during pregnancy or menopause). These variations demonstrate the significance of analyzing laboratory results in the consideration of the patient’s full medical problem together with his/her clinical symptoms.
- What if my T3, T4, or TSH levels are abnormal? An abnormal test may suggest thyroid dysfunction; however, additional tests or procedures will be necessary to diagnose the condition causing the thyroid disorder. Your primary physician may give other diagnostic examinations, radiological studies or changes in the course of treatment that result from the results.
Conclusion
To sum up, examining T3, T4, and TSH are for detecting and managing any thyroid conditions. Through the measurement of hormone levels and the ensuing appreciation, healthcare professionals will be well-placed to craft appropriate treatment programs to ensure positive patient outcomes. Whether you’re undergoing thyroid function abnormalities indication or looking for standard monitoring, interacting with an authoritative healthcare practitioner is the first successful treatment towards attaining thyroid wellness.