Diesel engines are complex machines, the inner workings of which are largely unknown even to most that operate them.
To make matters worse, the mechanical operations of diesel engines are fraught with confusing acronyms. Take, for instance, the DPF, SCR, and DOC filters of the exhaust aftertreatment system – what are these, and why do they matter?
We’re going to unpack some of that right here.
What Are the Differences Between DPF, SCR, and DOC Filters?
Understanding the differences between a Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC), Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF), and Selective Catalyst Reduction (SCR) is essential for making informed decisions when servicing exhaust aftertreatment systems. These components are often used in combination with each other to reduce exhaust emissions, and understanding how they work together is key to keeping your vehicle running clean and efficiently.
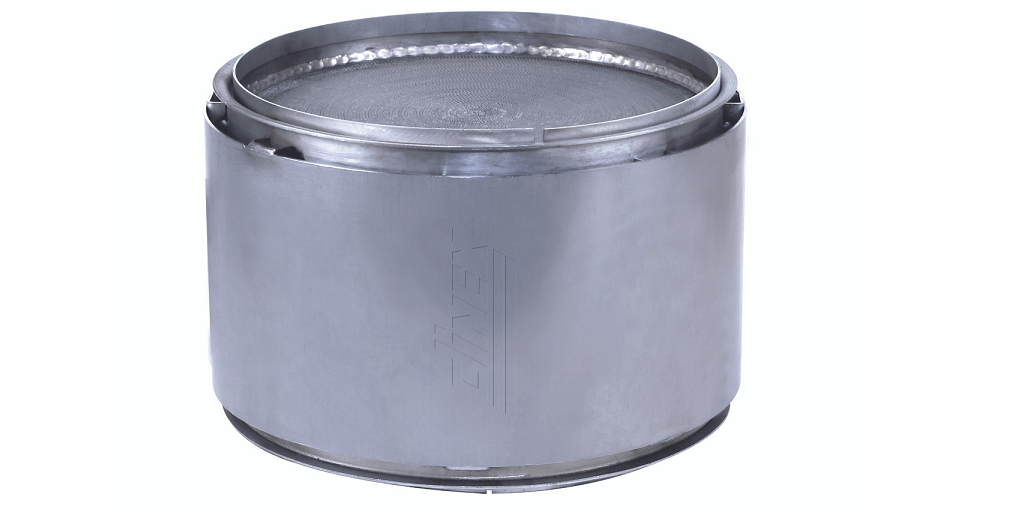
A DOC, sometimes referred to as a DOC filter, is a component of an exhaust aftertreatment system that works to reduce the emission of hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. It uses a chemical reaction to break down these pollutants into harmless substances like carbon dioxide and water. The DOC works by oxidizing the pollutants, meaning it adds oxygen atoms to the molecule to break it down. This process is called oxidation-reduction, or redox, and is a key part of the exhaust aftertreatment system.
A DPF, or diesel particulate filter (AKA DPF filter), works to reduce the emission of particulate matter (PM) from diesel engines. It captures particles in the exhaust and prevents them from entering the atmosphere. This helps reduce air pollution and improve air quality. The DPF works by capturing the particles on a filter and then burning them off in a process called regeneration.
An SCR, or selective catalyst reduction, works to reduce the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx). It works by injecting a reducing agent, typically urea, into the exhaust stream. The urea reacts with the NOx to form harmless nitrogen and water. The SCR is often used in combination with a DOC and DPF to further reduce emissions.
Together, these components of a diesel engine’s exhaust aftertreatment system help reduce diesel emissions while also improving the performance and longevity of the engine.
Does a DOC Filter Need to Be Cleaned Like a DPF?
So, does a DOC need to be cleaned? The answer is yes, but it depends on the type of DOC and the application. Most DOCs require regular maintenance and cleaning to ensure they are functioning properly. Just like a diesel DPF filter, it’s advisable to have your DOC filter cleaned or serviced about every 200,000 miles, or sooner if necessary. It’s good practice to have them serviced or cleaned at the same time to keep them on the same schedule. It’s also important to understand the type of DOC you have and the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and cleaning.
Where Can You Find Quality DOC Filters Online?
Looking for high-quality DPF or DOC filters? Visit Filter Service and Supply online via the previous link. They carry a wide range of high-quality diesel exhaust aftertreatment system components, including but not limited to DPF and DOC filters from Dinex Emissions, Skyline Emissions, and FSS Emission Products. They also carry gaskets and sensors and they even offer DPF filter cleaning services.
For more information, visit their website or contact them at 760-455-0263.
For More Information about Dpf Filter Replacement and Cummins Isx Dpf Filter PLease Visit: Filter Service and Supply